CSS Position property helps to position the element in the HTML page. It can be used to position the element from its existing position to anywhere on the page depending on which of the positioning method is used.
The different position values are:
position: static
All the elements are positioned static by default. The element with position: static are not positioned in any specific way. They are positioned according to the normal flow of the page. ie. top to bottom
top, bottom, left, right properties do not affect the elements which are positioned as static
child: {
position: static; /*Default No need to specify explicitly*/
top: 100px; /* wont effect the position */
}position: relative
The element which is position: relative are positioned from its normal position.
Just setting position: relative doesn’t actually move the element from the normal position. top, bottom, right, left properties are used to move the element
* Note: the gaps left by the element when moved from its normal position using position: relative cannot be occupied by the other elements (given that they are not positioned differently)
.child {
position: relative;
left: 70px;
}The above code block will move the element from its normal position to left by 70px
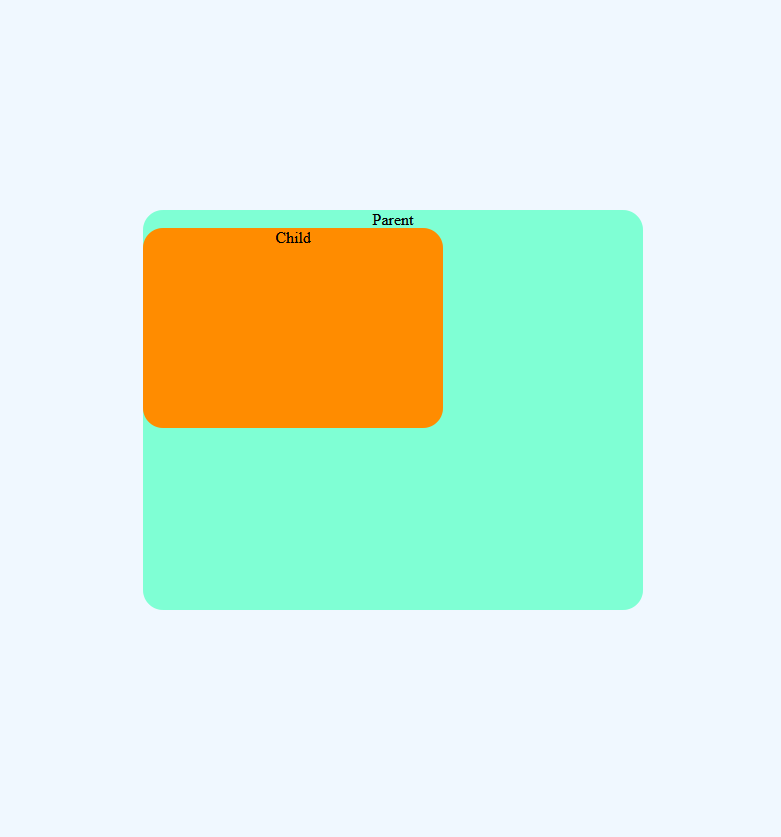
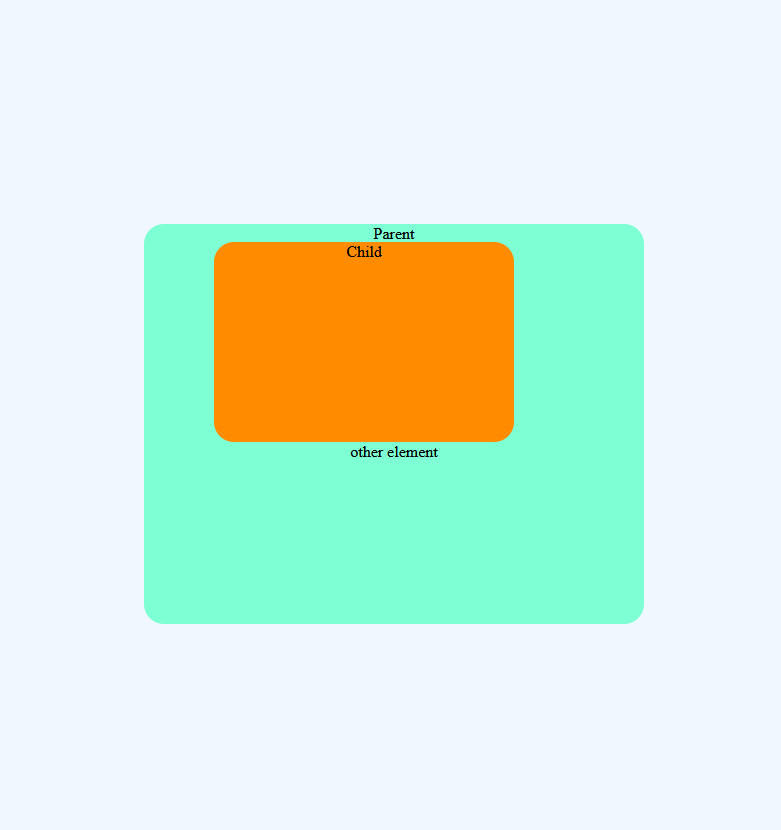
position: absolute
The element which is position: absolute will be positioned relative to the one of the nearest parent (which is positioned to a value other than static) and if no such parent is found then it is positioned relative to the document
This may have been confusing to understand. let us understand with an example
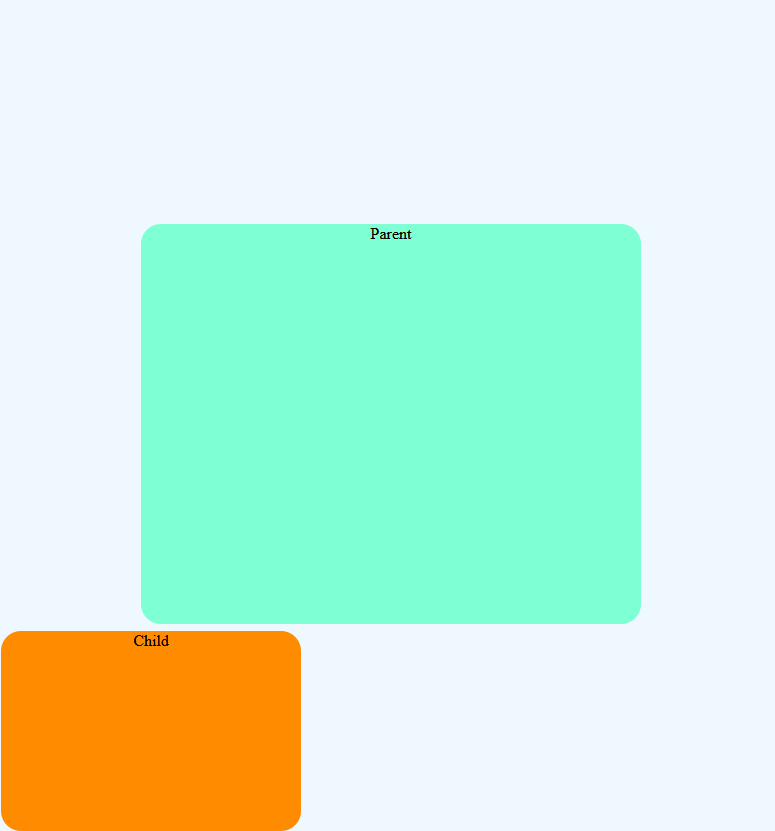
/*Here Parent element is not positioned explicitly*/
.parent {
height: 400px;
width: 500px;
background-color: aquamarine;
}
.child {
height: 200px;
width: 300px;
background-color: darkorange;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
}In the above example, the parent element is not positioned in any of the ways so now the child element will behave in a way that it has no parent element and it will be positioned to the left bottom of the HTML page
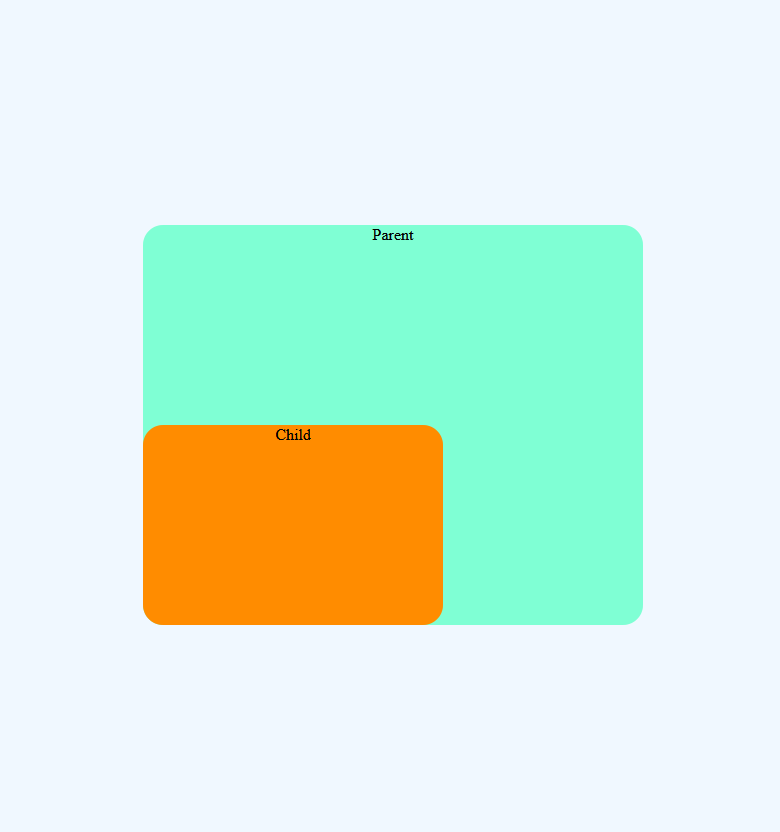
/*Here Parent element is positioned as relative*/
.parent {
position: relative;
}
.child {
position: absolute;
height: 400px;
width: 500px;
background-color: aquamarine;
}Now in the above example, the parent element is positioned relatively so now the child element will move to the bottom left of the parent element
Note: There is no gap left by the element at its normal position unlike position: relative
position: fixed
The element which is position: fixed are positioned always relative to the viewport and is not affected by the scrolling of the page
Element is positioned using top, bottom, left, right properties
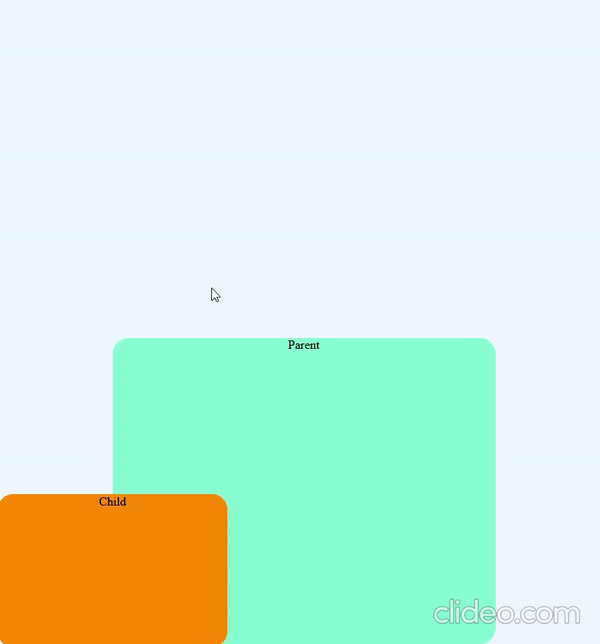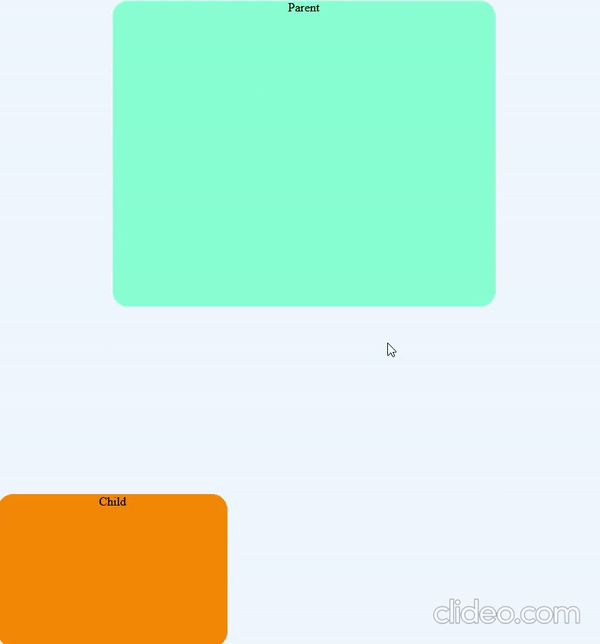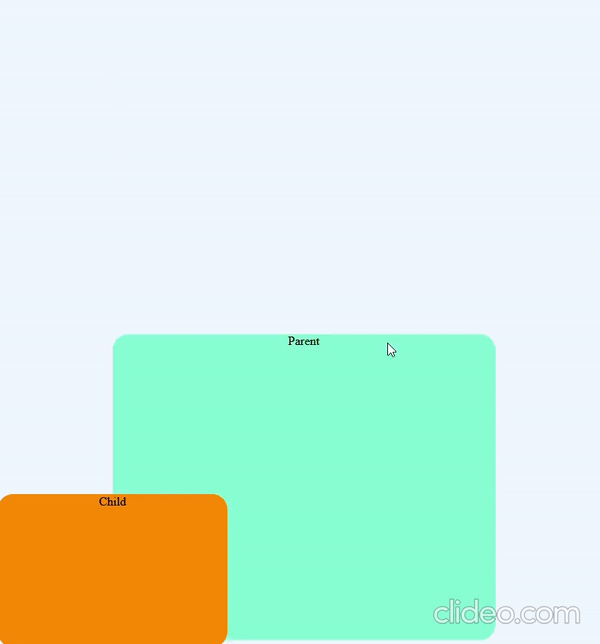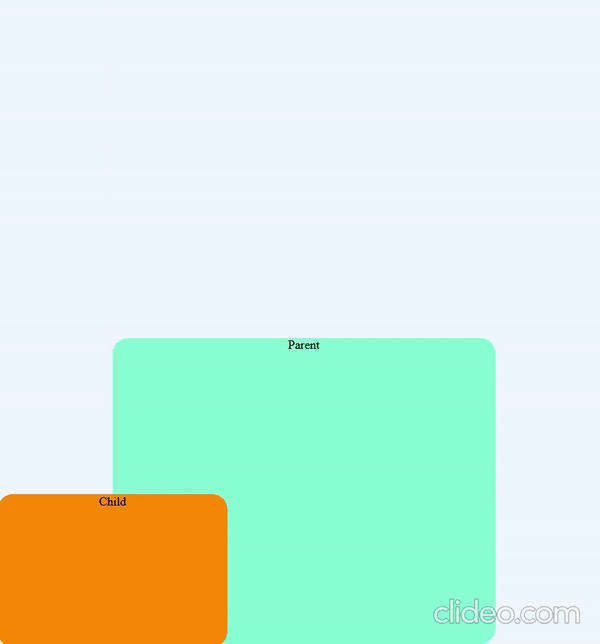
.child {
position: fixed;
bottom: 0px;
left: 0px;
}position: sticky
The element which is position: sticky is positioned at a fixed position when it reaches the offset provided
Element is actually at the normal position and as soon as while scrolling the specified offset is reached it get fixed to that position
top, bottom, right, left properties are used to position the element

.child {
position: sticky;
top: 0;
}Note: for safari use position: -webkit-sticky;
Suggestion:
You can checkout flexbox model which also helps to position the element in some way
Reference: